| Object name: | Constellation: | Coordinates: | Apparent size: | Visual brightness: |
|---|---|---|---|---|
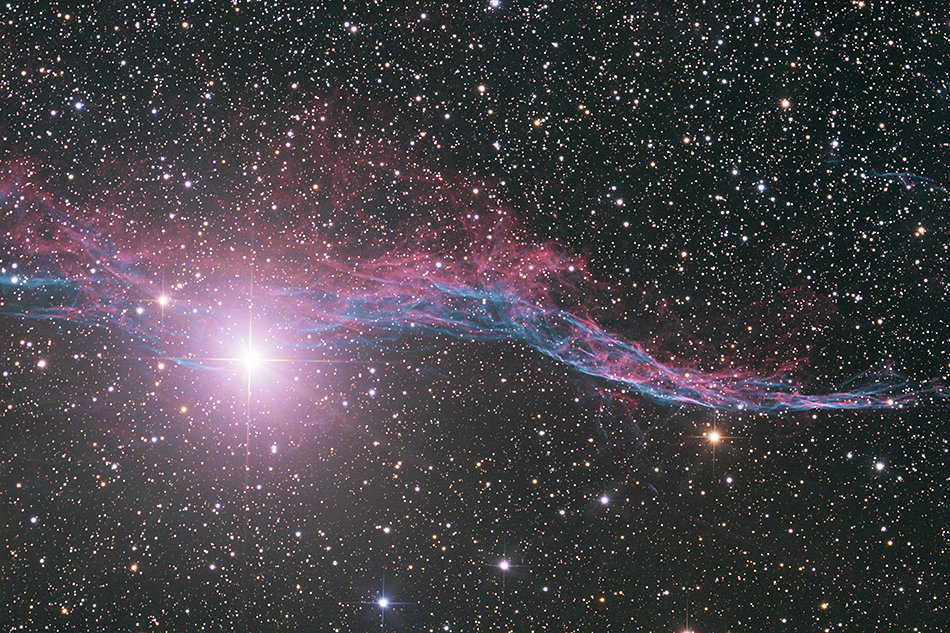
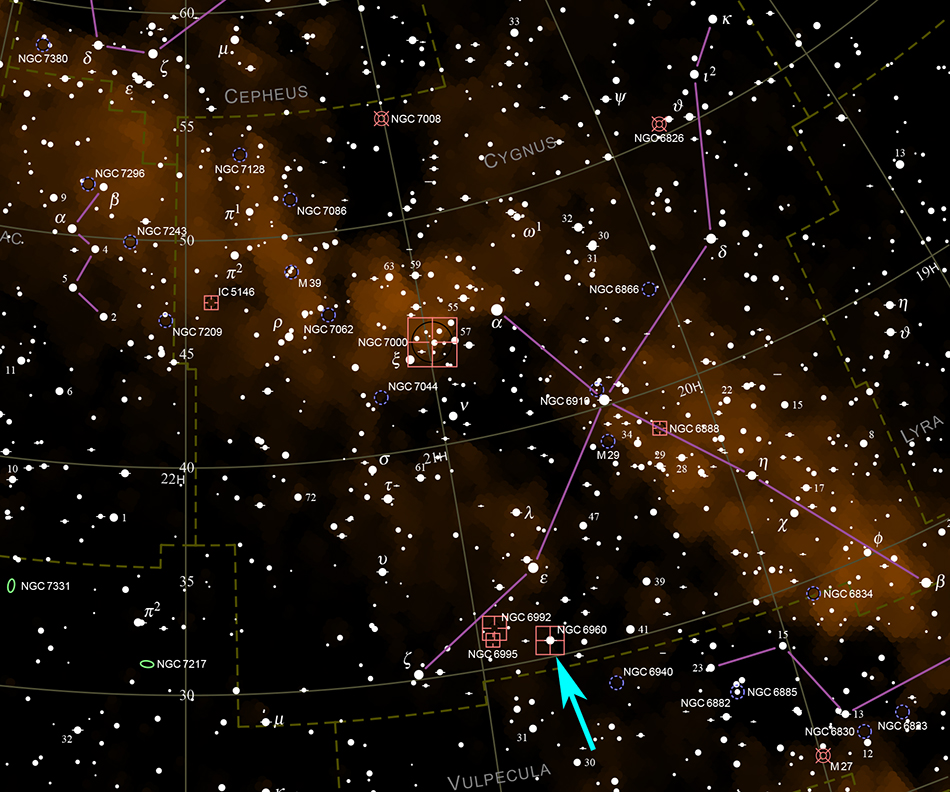
| NGC NGC 6960 | Cygnus | 20h46m / +30°43' | 70' x 6' | <7 mag (?) |
The supernova remnant NGC 6960 (Veil nebula, Western Veil nebula, Cirrus nebula, Witch's Broom nebula) in the constellation Cygnus. Discovered by the German-born British astronomer William Herschel in 1784, this cloud of heated and ionized gas is the result of a supernova which exploded some 5,000-10,000 years ago. The nebula is 2,400 light-years from Earth. The brightest star in the image is 4.2-magnitude 52 Cygni. It is a foreground star (291 light-years from earth) which can be seen by the naked eye (source: Wikipedia).
Fifty 3-minute exposures (150 minutes total exposure) at gain 100, taken on September 8 / 9, 2023 were added for this shot with Astro Pixel Processor (APP) software and the final image processing was done in Photoshop. Darks, flats, bias and darkflats were used.
Equipment: Cooled ASI 2600MC Pro camera, TeleVue Paracorr Type II coma corrector, 16" f/4.5 "Ninja" dobsonian telescope riding on a dual-axis Tom Osypowski equatorial platform, Lacerta MGEN autoguider, Lacerta off axis system (field of view comparison: image of the moon with the same equipment).